ANINUALE H06 Wireless Earbuds - Affordable Quality
Update on Sept. 13, 2025, 7:33 a.m.
We take for granted the small miracles of modern life. Chief among them is the personal bubble of sound created by a pair of wireless earbuds. It’s a seamless, invisible thread connecting us to music, podcasts, and conversations, effortlessly tuning out the world’s chaos. We call it “pairing,” a deceptively simple term for a profoundly complex technological dance. But this isn’t magic; it’s a symphony of applied physics and meticulous engineering, packed into a shell of plastic smaller than a fingertip.
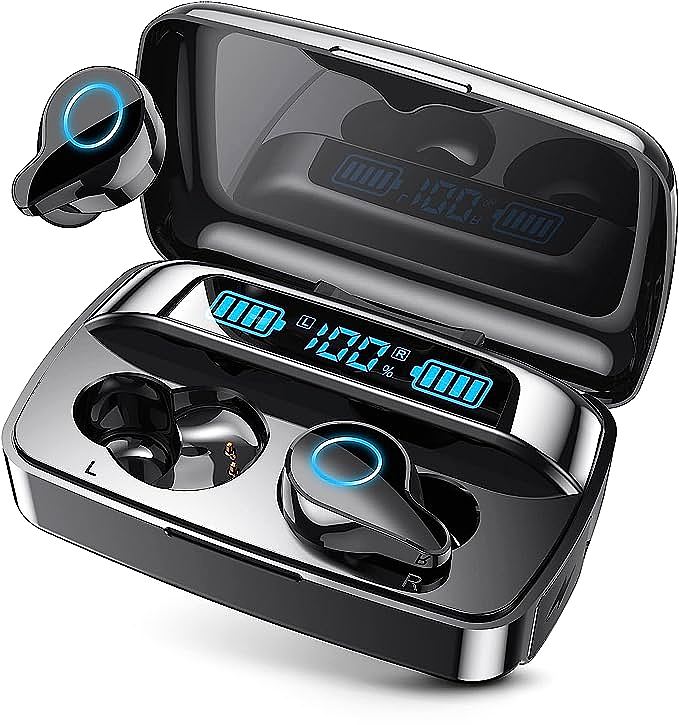
To truly understand it, let’s place a common, accessible pair of earbuds—like the ANINUALE H06—on our virtual workbench. We’re not here to review it. We’re here to dissect it, to peel back its layers and reveal the elegant scientific principles that power not just this device, but nearly every wireless audio gadget you encounter. This is a journey into the science you use every day, but may have never truly seen.

The Unseen Symphony: Taming the Airwaves
The first principle we encounter is the most ethereal: the connection itself. These earbuds boast Bluetooth 5.3, a version number that, to most, is just a bigger number than the last. Yet, the leap from earlier standards to 5.3 is less about raw speed and more about intelligence and efficiency in managing a very crowded space.
Imagine you’re in a room where a dozen different conversations are happening at once. Early wireless technology was like trying to have a clear conversation in the middle of that chaos; signals would cross, interfere, and result in stuttering, frustrating dropouts. Bluetooth 5.3, however, acts as a masterful conversation moderator. It employs an enhanced channel classification system that is constantly scanning the 2.4 GHz frequency band—the same crowded highway used by Wi-Fi, microwaves, and countless other devices. It intelligently identifies “noisy” channels and swiftly hops to clearer ones, ensuring the data stream for your music remains stable and coherent. This is why a modern pair of earbuds can maintain a rock-solid connection on a packed subway train, a feat that was once a gamble.
This intelligence also tackles latency, the perceptible delay between a video playing on your screen and the sound reaching your ears. By optimizing how data packets are scheduled and transmitted, Bluetooth 5.3 dramatically shortens this delay, eliminating the annoying lip-sync problem that plagued older devices and making wireless audio viable for gaming and movies.
Perhaps most importantly, it’s incredibly power-efficient. It lays the groundwork for LE Audio, the next generation of Bluetooth, and its highly efficient LC3 codec, which promises to deliver higher-quality audio while consuming even less energy. While not yet universally implemented, the architecture of Bluetooth 5.3 is built with this future in mind, treating battery life as a precious, finite resource.

The Pocket-Sized Power Plant: Chemistry in a Box
This brings us to the physical heart of the device: its power source. A claim of “60-hour playtime” seems almost absurd for something so small. This endurance isn’t just about a big battery; it’s the result of a beautiful synergy between chemistry and smart power management.
Inside the earbuds and their case are lithium-ion batteries. Their key advantage is a high energy density. Think of it as the ability to pack a massive amount of energy into a tiny, lightweight container. The lithium ions, the charge carriers, are incredibly small and can be packed tightly into the battery’s anode and cathode materials. The charging case acts as a mothership, a larger fuel depot that recharges the smaller scout ships (the earbuds) several times over.
But the raw capacity of the battery is only half the story. The other half is the silent, vigilant work of the Battery Management System (BMS). This tiny integrated circuit is the unsung hero of every modern rechargeable device. It’s a microscopic guardian, constantly monitoring voltage, current, and temperature. The BMS prevents the battery from overcharging, which could cause damage and even thermal runaway, and from over-discharging, which can permanently reduce its capacity. It’s the smart engine governor that ensures the pocket-sized power plant operates not only for a long time, but also safely and for many charge cycles. The LED display on the case is a simple but crucial window into this system, translating complex electrical data into a single, understandable metric that frees us from “charge anxiety.”

The Engineered Shell: Surviving the Physical World
From the invisible world of radio waves and the chemical world of batteries, we move to the physical reality of daily use. An IPX7 waterproof rating sounds technical, but it represents a triumph of mechanical and materials engineering. The “IP” stands for Ingress Protection, a universal standard (IEC 60529) that grades a device’s resistance to solids and liquids. The ‘X’ means it wasn’t tested for dust, but the ‘7’ is the crucial number for water. It certifies that the device can be fully submerged in 1 meter of fresh water for up to 30 minutes without failing.
Achieving this is like building a miniature submarine. Engineers must create a perfect seal against a relentless, pressure-seeking enemy. This is often accomplished through a combination of methods. Precision-molded plastic shells are designed to fit together with microscopic tolerances. Tiny, custom-shaped rubber gaskets, or O-rings, are compressed into channels where parts meet, forming a physical barrier. In some cases, the seams of the casing are fused together using ultrasonic welding, which vibrates the plastic until it melts and re-forms as a single, solid piece.
Furthermore, a final line of defense is often applied directly to the electronics inside: a hydrophobic nano-coating. This is a transparent layer, thousands of times thinner than a human hair, that repels water at a molecular level. Should any moisture breach the outer shell, this coating prevents it from short-circuiting the delicate circuitry. It’s this multi-layered defense that gives you the confidence to sweat through a workout or get caught in a rainstorm without a second thought.
The Art of Vibration: Crafting the Sound You Hear
Finally, we arrive at the entire point of the device: sound. The promise of “deep bass” comes from the most common type of audio transducer in headphones, the dynamic driver. It is, in essence, a perfect, miniature version of a massive concert loudspeaker.
It works on a fundamental principle of electromagnetism. A small coil of wire (the “voice coil”) is attached to a thin, flexible cone (the “diaphragm”). This assembly is suspended in front of a permanent magnet. When the electrical signal of your music flows through the voice coil, it generates a fluctuating magnetic field. This field interacts with the field of the permanent magnet, causing the coil and the attached diaphragm to vibrate rapidly back and forth. These vibrations push and pull the air, creating the pressure waves that travel down your ear canal and are interpreted by your brain as sound.

The character of that sound is a deliberate engineering choice. A larger diaphragm can move more air, which is more effective at producing the long, powerful waves of low-frequency bass notes. The material of the diaphragm—be it paper, plastic, or a more exotic composite—affects the rigidity and speed of its vibrations, influencing the clarity of midrange and treble frequencies.
The term “deep bass” is a description of a specific tuning. If you were to look at the earbud’s frequency response curve—a graph showing how loudly it plays each tone from low to high—you would likely see a noticeable bump in the lower frequency range. This is an intentional choice made by the audio engineers to create a sound signature that is impactful and engaging for genres like pop, hip-hop, and electronic music. It is a trade-off, as an over-emphasized bass can sometimes cloud the detail in vocals or cymbals. There is no single “perfect” tuning; it is an art form, a decision about the kind of emotional experience the engineers want to deliver.

When you pull these components apart—the intelligent radio, the dense chemical battery, the sealed physical shell, and the vibrating acoustic driver—you realize a pair of wireless earbuds is not a single product. It’s a convergence. It is a marvel of integration, where advances in materials science, wireless communication, electrochemistry, and acoustic physics come together to create something that is profoundly greater than the sum of its parts. The next time you press play, take a moment to appreciate the invisible symphony of science happening just inches from your brain.