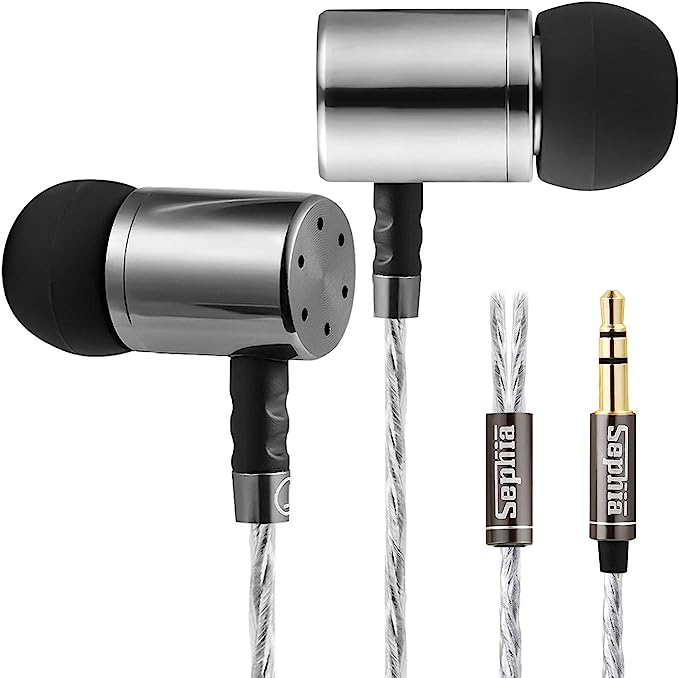
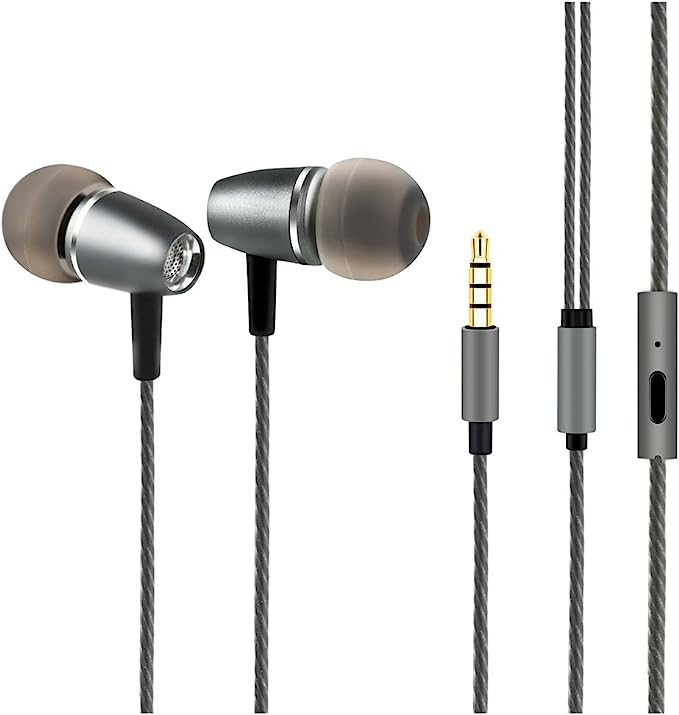
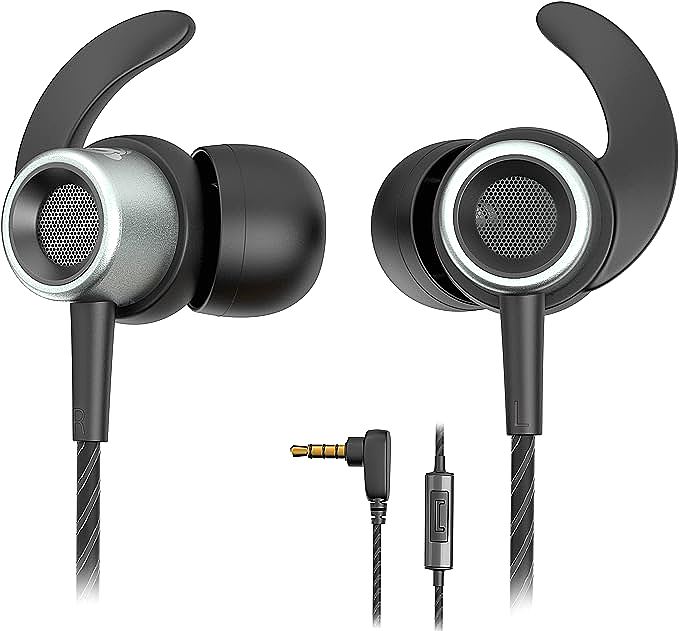
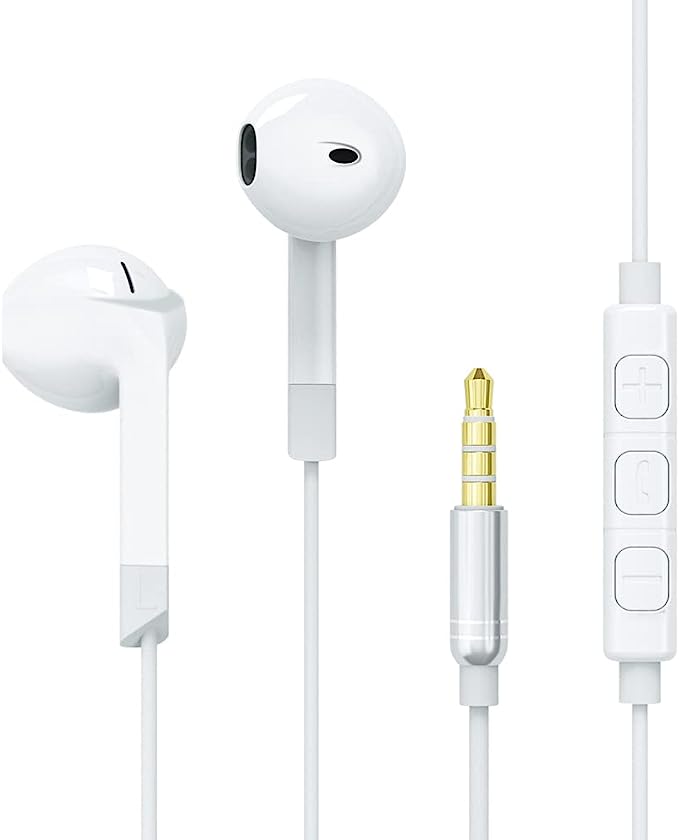
Accessonico Wired Earbuds: Reliable Sound for Your Kindle Fire and Android Devices
Update on March 20, 2025, 5:28 p.m.
In an era dominated by wireless technology, it’s easy to dismiss wired earbuds as relics of the past. Bluetooth headphones and earbuds offer undeniable convenience, freeing us from the tangle of cords. Yet, amidst the wireless revolution, a quiet resurgence is underway. Audiophiles, gamers, and everyday users are rediscovering the enduring benefits of wired sound. The Accessonico Wired Earbuds exemplify this trend, offering a compelling combination of simplicity, reliability, and, most importantly, audio fidelity. But why, in a world of wireless freedom, do wired earbuds continue to hold their own? The answer lies in the fundamental principles of sound reproduction and the inherent limitations of wireless technology.

Decoding Sound: The Fundamentals of Wired Audio
Before we delve into the specific advantages of wired earbuds, it’s essential to understand the basics of how audio is transmitted and reproduced. This journey begins with the seemingly humble 3.5mm jack, a connector that has been a cornerstone of audio technology for decades.
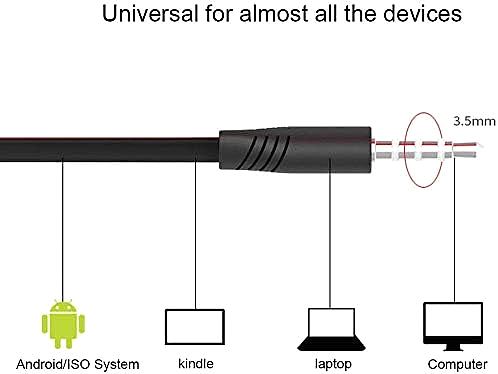
The Venerable 3.5mm Jack: A Closer Look at TRS and TRRS
The 3.5mm headphone jack, also known as a phone connector, is a ubiquitous sight on smartphones, tablets, laptops, and countless other devices. It’s a marvel of miniaturization, packing multiple electrical contacts into a compact, standardized design. But there’s more to this connector than meets the eye. There are two primary types: TRS and TRRS.
- TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve): This type has three conductors: the tip, the ring, and the sleeve. These correspond to the left audio channel, the right audio channel, and the ground, respectively. TRS connectors are typically used for stereo headphones without a microphone.
- TRRS (Tip-Ring-Ring-Sleeve): This version adds an extra ring, bringing the total number of conductors to four. The additional ring is commonly used for a microphone signal, allowing for headsets with both audio playback and voice input capabilities. The order of the microphone and ground connections can vary, leading to two main standards: CTIA (used by most Android devices and Apple) and OMTP (used by some older devices). The Accessonico Wired Earbuds, with their 3.5mm connector, are designed for broad compatibility across devices using the CTIA standard.
The standardization of the 3.5mm jack has been crucial to its enduring success. It provides a universal interface for connecting headphones and other audio devices, regardless of manufacturer. This plug-and-play simplicity is a key advantage of wired technology.
Analog vs. Digital: A Tale of Two Signals
The method of signal transmission is where wired and wireless headphones fundamentally differ. Wired headphones, like the Accessonico model, rely on analog signals, while wireless headphones use digital signals. Understanding this distinction is crucial to appreciating the nuances of audio quality.
- Analog Signals: An analog signal is a continuous electrical signal that directly represents the sound wave. Imagine a vinyl record: the grooves on the record are a physical representation of the sound wave, analogous to the electrical signal in a wired headphone. The voltage of the signal varies continuously, mirroring the fluctuations in air pressure that create sound.
- Digital Signals: A digital signal, on the other hand, represents sound as a series of discrete numbers (bits). This process involves sampling the analog signal at regular intervals and quantizing the amplitude of the signal at each sample point. Think of it like a digital photograph: the image is made up of many tiny pixels, each with a specific color value. Similarly, a digital audio signal is made up of many tiny “snapshots” of the sound wave.
The conversion from analog to digital (and back again) is a necessary step for wireless transmission, but it’s not without its consequences.
Audio Codecs: From MP3 to FLAC
When audio is transmitted wirelessly via Bluetooth, it’s typically compressed using an audio codec. A codec is an algorithm that encodes and decodes digital audio data. Compression is necessary to reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted, conserving bandwidth and battery power. However, many codecs are lossy, meaning that some audio information is discarded during the compression process.
- MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer III): One of the oldest and most widely used lossy codecs. It achieves significant file size reduction but can sacrifice audio quality, especially at lower bitrates.
- AAC (Advanced Audio Coding): Generally considered superior to MP3, AAC is used by Apple’s iTunes and many other streaming services. It offers better sound quality at similar bitrates.
- SBC (Subband Coding): The mandatory codec for Bluetooth audio. It’s a relatively low-complexity codec, meaning it doesn’t require a lot of processing power, but its audio quality is generally considered to be inferior to AAC and aptX.
- aptX: A family of proprietary codecs developed by Qualcomm. aptX aims to provide higher-fidelity audio than SBC, with lower latency. There are several variations, including aptX, aptX HD, and aptX Adaptive.
- FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec): Unlike the others listed, FLAC is a lossless codec. This means that it compresses audio data without discarding any information. When a FLAC file is decoded, it’s bit-for-bit identical to the original source. Of course, lossless codecs result in larger file sizes.
While wireless codecs have improved significantly, they still introduce a layer of processing that can potentially degrade the audio signal. Wired headphones, by transmitting the audio in its raw, analog form, bypass this potential bottleneck.
The Wired Advantage: Unpacking the Benefits
With the fundamentals of wired audio in mind, let’s explore the key advantages that keep wired earbuds, like the Accessonico model, relevant in today’s market.
The Purity of Sound: Lossless Transmission and Low Distortion
The most significant advantage of wired headphones is their potential for superior audio fidelity. Because the signal remains analog from the source device to the headphone drivers, there’s no digital conversion or compression to introduce artifacts or degrade the sound. The electrical signal directly drives the headphone diaphragm, creating sound waves that closely mirror the original recording.
This lossless transmission minimizes the potential for distortion, which refers to any unwanted alteration of the audio signal. Distortion can manifest as muddiness, harshness, or a lack of clarity. While all headphones exhibit some degree of distortion, well-designed wired headphones can achieve extremely low levels, resulting in a more accurate and transparent sound reproduction.
Zero Latency: Perfect Synchronization for Gaming and Video
Another significant advantage of wired headphones is the absence of latency. Latency refers to the delay between when an audio signal is sent and when it’s heard. Wireless headphones, due to the need to encode, transmit, and decode the audio signal, inevitably introduce some latency. This delay might be imperceptible for casual music listening, but it can be highly detrimental for gaming and video, where precise synchronization between audio and visuals is crucial.
Imagine playing a fast-paced video game where the sound of a gunshot lags behind the visual action. This delay can disrupt your timing and reaction time, negatively impacting your performance. Similarly, when watching a movie, audio latency can cause lip-sync issues, where the actors’ words don’t match their mouth movements. Wired headphones, with their direct, instantaneous signal transmission, eliminate this problem entirely.
Never Run Out of Power: The Simplicity of a Wired Connection
Wired headphones offer a level of simplicity and reliability that wireless models can’t match. They don’t require batteries, so you never have to worry about running out of power in the middle of a listening session. They don’t need to be paired with your device, eliminating the occasional frustrations of Bluetooth connectivity issues. Simply plug them in, and you’re ready to go. This plug-and-play functionality is particularly appealing for users who value ease of use and reliability above all else.

Accessonico Wired Earbuds
The Accessonico wired earbuds, are designed with keeping some of the best features of wired earphone.
Lightweight and comfortable
Weighing only 0.634 ounces, and with dimensions of 2.99 x 2.91 x 0.75 inches, Accessonico wired earbuds are very comfortable to wear.
Universal Compatibility
Accessonico wired earbuds support almost all devices with 3.5mm audio jack, which include, but not limited to: Kindle Fire, Fire HD 8, HD 10 Plus, Samsung, LG, Fire 7 Tablet, and other Smart Android Cell Phones.
Beyond the Basics: A Deeper Dive into Headphone Technology
While the Accessonico Wired Earbuds are designed for simplicity and ease of use, understanding some of the underlying technical principles can help you appreciate the nuances of headphone performance and make more informed choices.
Impedance Matching: Finding the Right Fit for Your Device
Impedance is a measure of a headphone’s resistance to electrical current. It’s measured in ohms (Ω). The impedance of a headphone interacts with the output impedance of the source device (phone, tablet, amplifier, etc.). Ideally, the output impedance of the source should be significantly lower than the impedance of the headphones. This is known as impedance matching, and it ensures efficient power transfer and optimal sound quality.
Mismatched impedance can result in reduced volume, altered frequency response, and increased distortion. While the specific impedance of the Accessonico Wired Earbuds is not provided in the available information, most consumer headphones with a 3.5mm jack are designed to work well with the low output impedance of portable devices like smartphones and tablets.
Sensitivity and Volume: Understanding the Relationship
Sensitivity is a measure of how loud a headphone will play at a given power level. It’s typically expressed in decibels of sound pressure level per milliwatt (dB SPL/mW) or decibels of sound pressure level per volt (dB SPL/V). Higher sensitivity means that the headphones will produce a louder sound for the same amount of power.
Sensitivity is an important factor to consider, especially if you’re using a low-powered device like a smartphone. Headphones with low sensitivity might not be able to reach adequate listening volumes on such devices. Again, while the specific sensitivity of the Accessonico earbuds is not stated, they are likely designed to be sufficiently sensitive for use with typical portable devices.
Frequency Response: Decoding the Sound Signature
Frequency response refers to the range of frequencies that a headphone can reproduce, and how accurately it reproduces them. It’s typically represented as a graph, with frequency on the horizontal axis (measured in Hertz, Hz) and amplitude (loudness) on the vertical axis (measured in decibels, dB).
An ideal frequency response would be a flat line, indicating that the headphones reproduce all frequencies equally. In reality, most headphones have some variations in their frequency response, which gives them a particular sound signature. Some headphones might emphasize bass frequencies, resulting in a “warm” or “boomy” sound. Others might emphasize treble frequencies, resulting in a “bright” or “crisp” sound. The preferred frequency response is largely a matter of personal preference. Without the specific frequency response graph for the Accessonico Wired Earbuds, it’s difficult to definitively characterize their sound signature, though user reviews suggest a clear and balanced sound.
A Brief History of Headphones
The history of headphones traces back to the late 19th century, predating even the widespread use of telephones. Early headphones were primarily used for telephone and radio communication, often by operators and military personnel. These early models were bulky and uncomfortable, a far cry from the sleek designs we see today.
The first headphones resembling modern designs appeared in the early 20th century. Nathaniel Baldwin, an American inventor, is often credited with creating some of the first commercially successful headphones in his kitchen. He sold them to the US Navy, which recognized their potential for communication.
The development of dynamic drivers in the 1930s revolutionized headphone technology. Dynamic drivers, which use a moving coil to create sound, are still the most common type of driver used in headphones today. The introduction of stereo sound in the 1950s further enhanced the listening experience.
The rise of portable music players, like the Walkman in the late 1970s and early 1980s, fueled the popularity of headphones for personal listening. Over the decades, headphones have continued to evolve, with advancements in materials, design, and technology, leading to the diverse range of options available today, from simple wired earbuds to sophisticated wireless noise-canceling models.
Caring for Your Wired Earbuds
To ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your Accessonico Wired Earbuds (or any wired earbuds), proper care is essential. Here are a few tips:
- Avoid Tangling: When not in use, neatly coil the cable to prevent tangling and stress on the wires. Consider using a cable organizer or a small pouch to store them.
- Clean Regularly: Earwax and debris can accumulate on the earbud tips. Clean them regularly with a soft, dry cloth or a cotton swab. For removable tips, you can detach them and wash them with mild soap and water. Make sure they are completely dry before reattaching them.
- Protect the Jack: The 3.5mm jack is a delicate component. Avoid bending or putting excessive pressure on the connector. When plugging and unplugging, grip the connector itself, not the cable.
- Store Properly: When storing your earbuds for an extended period, keep them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Handle with Care: While wired earbuds are generally more durable than wireless ones in some respects, they are still susceptible to damage from drops, impacts, and excessive pulling on the cable.
Conclusion
The Accessonico Wired Earbuds represent a return to the fundamental principles of high-quality audio reproduction. In a world increasingly dominated by wireless convenience, they offer a refreshing reminder of the enduring benefits of a wired connection: pristine analog sound, zero latency, and unwavering reliability. While they may lack the bells and whistles of some high-end wireless models, they deliver a pure and unadulterated listening experience that is both satisfying and accessible. They are a testament to the fact that sometimes, the simplest solution is the best, providing a direct, uncompromised path from your audio source to your ears. For those who prioritize sound quality, simplicity, and value, the Accessonico Wired Earbuds are a worthy choice, demonstrating that the wired connection is far from obsolete. It’s a connection to the essence of sound itself.























































