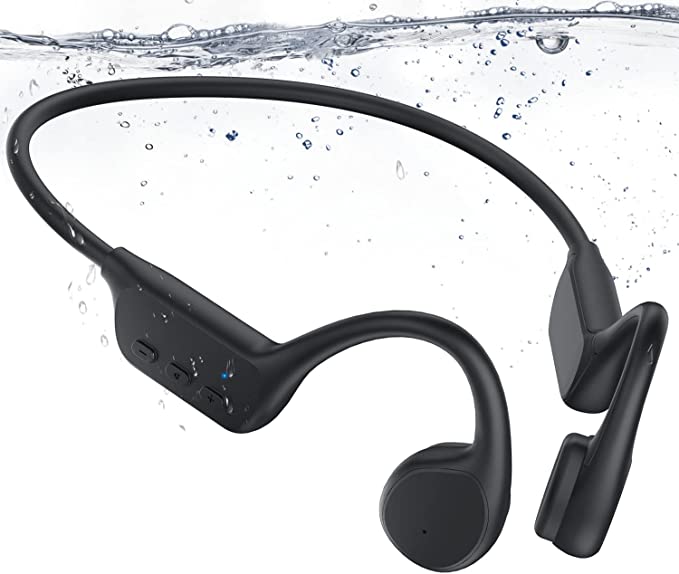
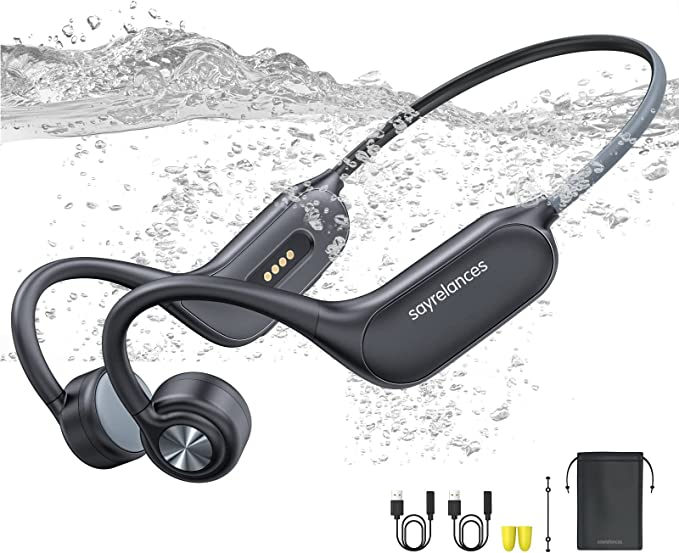
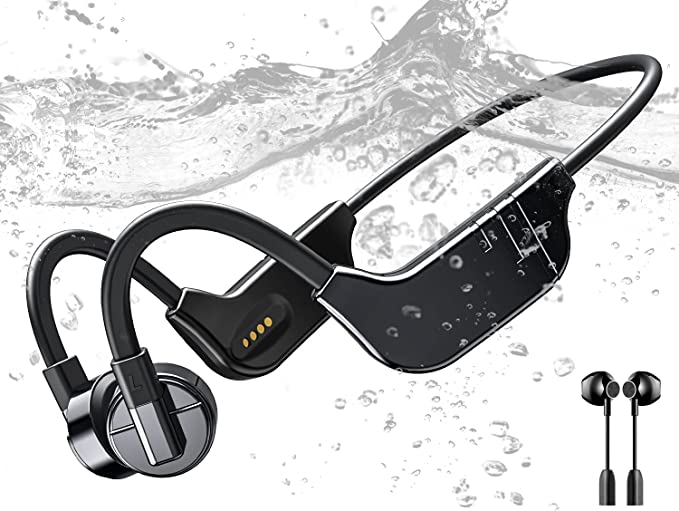
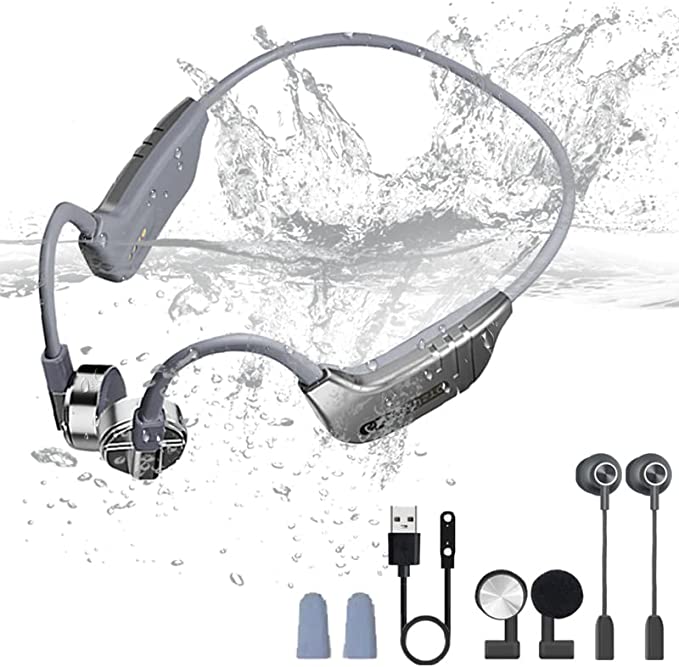
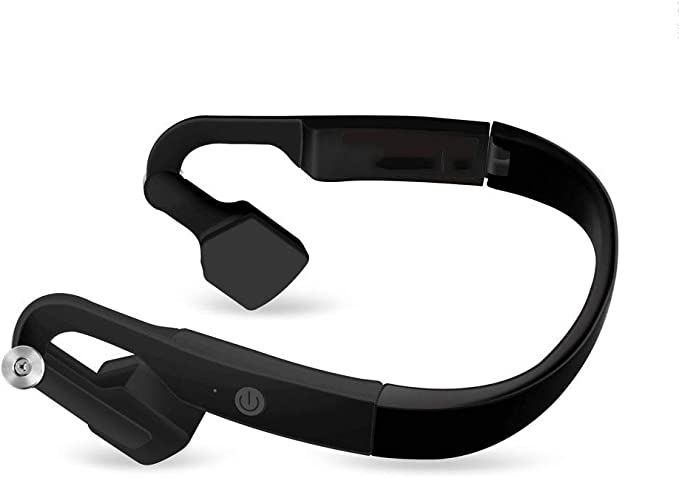
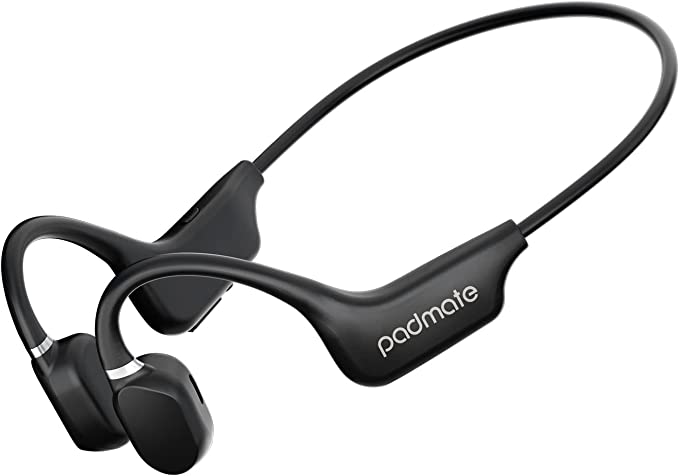
CTM ORUN1 Wireless Bone Conduction Headphones: Stay Safe and Connected While Enjoying Your Music
Update on March 8, 2025, 5:17 a.m.
Imagine this: you’re jogging through a park, sunlight dappling through the leaves. Your favorite playlist fuels your stride, but you’re also acutely aware of the cyclist approaching from behind, the laughter of children playing nearby, and the gentle rustling of the wind. You’re experiencing the best of both worlds – immersed in your music, yet fully connected to your surroundings. This is the promise of bone conduction technology, and it’s beautifully exemplified by the CTM ORUN1 headphones.
The Sound Around Us, and How We Hear
Before diving into bone conduction, let’s quickly recap how traditional hearing works. Sounds are essentially vibrations that travel through the air. These vibrations enter our ear canal, causing the eardrum to vibrate. These vibrations are then amplified by tiny bones in the middle ear (the malleus, incus, and stapes) and transmitted to the cochlea, a fluid-filled, snail-shaped structure in the inner ear. Within the cochlea, thousands of tiny hair cells convert these vibrations into electrical signals, which are then sent to the brain via the auditory nerve, where they are interpreted as sound. This is air conduction, the primary way we experience most sounds.
Bone Conduction: A Different Approach
Bone conduction, however, takes a different route. Instead of relying on air to transmit sound waves, it utilizes the bones of the skull. Vibrations are transmitted directly through the cheekbones (or other skull bones) to the cochlea, bypassing the eardrum and middle ear entirely.
It might sound strange, but you’ve likely experienced bone conduction firsthand. Ever noticed how your own voice sounds different when you hear a recording of it? That’s partly because when you speak, you hear your voice through both air conduction (the sound waves traveling through the air to your ears) and bone conduction (the vibrations of your vocal cords traveling through your skull). The recorded voice, lacking the bone-conducted component, sounds different – often higher-pitched – than what you’re used to.

Diving Deeper: The Science of Bone Conduction
The physics behind bone conduction is fascinating. Bone, while seemingly solid, is actually a surprisingly good conductor of vibrations. When a bone conduction transducer (the part of the headphones that generates the vibrations) is placed against the skull, it creates tiny vibrations that travel through the bone. These vibrations reach the cochlea, stimulating the hair cells just as air-conducted sound would.
There are different types of bone conduction transducers, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some use piezoelectric materials, which change shape when an electrical signal is applied, creating vibrations. Others use magnetostrictive materials, which change shape in response to a magnetic field. The specific type of transducer used can affect the sound quality, power efficiency, and size of the headphones.
It’s also worth noting that bone conduction isn’t completely isolated from air conduction. At higher volumes, some sound may “leak” and be transmitted through the air, potentially audible to those nearby. This is one of the inherent challenges of bone conduction technology.
CTM ORUN1: A Practical Example
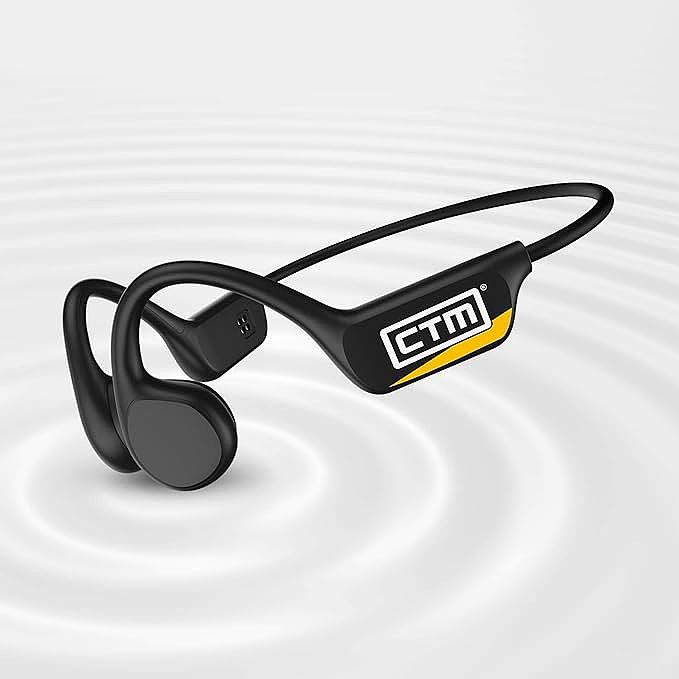
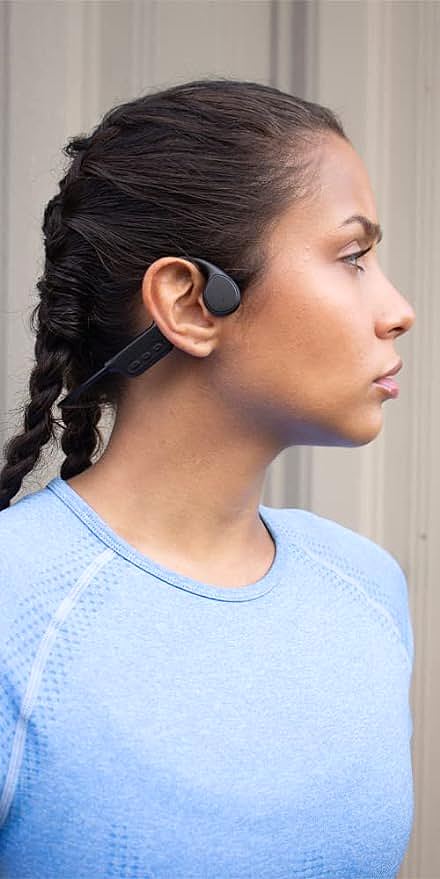
The CTM ORUN1 Wireless Bone Conduction Headphones, designed by Clear Tune Monitors (CTM), provide a clear illustration of how this technology works in practice. These headphones are designed to rest comfortably on your cheekbones, just in front of your ears, leaving your ear canals completely open. This “open-ear” design is a key feature, and a primary benefit, of bone conduction.

Design and Features
The ORUN1 features a lightweight, wraparound titanium frame. Titanium is known for its strength, durability, and flexibility, making it an ideal material for headphones that need to be both robust and comfortable. The frame is designed to gently but securely hold the transducers against your cheekbones, ensuring optimal sound transmission.
The open-ear design not only enhances safety but also provides a more comfortable listening experience for many users, especially during extended wear. There’s no pressure on the ear canal, and no feeling of isolation that can come with traditional earbuds or over-ear headphones.

Deeper into ORUN1
Let’s explore some of the specific technologies that power the ORUN1:
-
IPX6 Waterproof Rating: This means the ORUN1 is protected against powerful water jets. You can confidently wear them in the rain or during intense, sweaty workouts without worrying about damage. The “IP” stands for “Ingress Protection,” and the “X” indicates that the device hasn’t been formally tested for dust protection (though it’s likely to offer some resistance). The “6” specifically refers to protection against high-pressure water jets from any direction.
-
Bluetooth 5.0 Connectivity: The ORUN1 utilizes Bluetooth 5.0, the latest major version of the Bluetooth wireless communication standard. Compared to earlier versions, Bluetooth 5.0 offers several advantages, including:
- Increased Range: Theoretically up to four times the range of Bluetooth 4.2, though real-world performance will vary depending on obstacles and interference.
- Faster Data Transfer: Up to twice the speed of Bluetooth 4.2, which can improve audio quality and reduce latency.
- Lower Power Consumption: This contributes to the ORUN1’s 4.5-5.5 hour battery life.
- Dual Audio: While not explicitly stated for the ORUN1, Bluetooth 5.0 supports connecting to two audio devices simultaneously. This could be a potential feature, though it’s not confirmed in the provided materials.
-
Microphone Sensitivity (-42dB ± 3dB): This specification refers to how well the microphone picks up sound. A sensitivity of -42dB ± 3dB is fairly typical for headphones and indicates decent performance for phone calls and voice assistant use. The lower the negative number, the more sensitive the microphone. The ±3dB indicates the tolerance – the actual sensitivity may vary slightly from unit to unit.
-
Frequency Response (80 ~ 5000Hz): This describes the range of frequencies the headphones can reproduce. The human hearing range is typically considered to be 20Hz to 20,000Hz. The ORUN1’s range of 80Hz to 5000Hz indicates that it will reproduce most of the critical frequencies for speech and music, though it will lack the very lowest bass frequencies and the highest treble frequencies. This is a common characteristic of bone conduction headphones, and it’s a trade-off for the open-ear design and other benefits. While audiophiles seeking the most accurate sound reproduction might prefer a wider frequency response, the ORUN1’s range is sufficient for casual listening and provides a clear and balanced sound for most users.

The User Experience: Beyond the Specs
Technical specifications are important, but they don’t tell the whole story. The real value of bone conduction headphones lies in how they feel and function in everyday life.
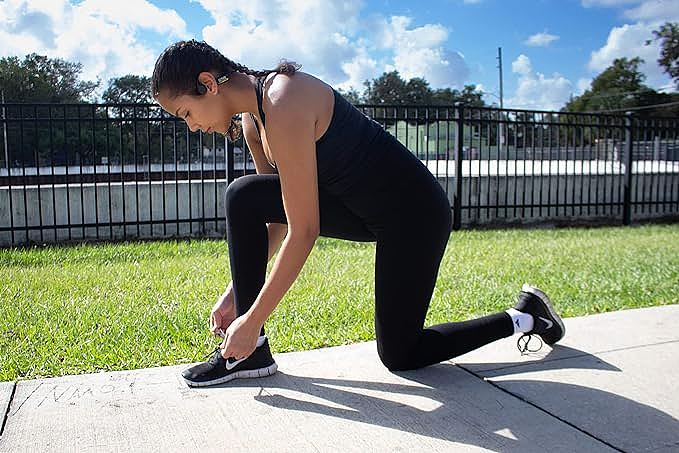
Imagine using the ORUN1 while:
- Cycling: You can hear the traffic around you, ensuring your safety, while still enjoying your favorite podcast or motivational music.
- Working in an office: You can listen to music or take calls without being completely cut off from your colleagues. You can still hear someone calling your name or asking a question.
- Hiking: You can enjoy the sounds of nature – birdsong, the rustling of leaves – while also listening to an audiobook or music.
- Running errands: You can stay aware of your surroundings while listening to a podcast or making phone calls.
This ability to stay connected to the world around you while enjoying audio is a game-changer for many people. It’s not just about convenience; it’s about safety and a more natural way of experiencing sound.
It is crucial to state that, since bone conduction headphones do not block the ear canal, the quality and volume of surrounding sounds will significantly impact the listening experience. In very noisy environments, it may be difficult to hear the audio clearly.
Addressing Potential Concerns
It’s important to acknowledge the limitations of bone conduction technology. While it offers many advantages, it’s not perfect.
- Sound Leakage: As mentioned earlier, some sound can leak from the transducers and be heard by people nearby, especially at higher volumes. This is less of an issue in outdoor or noisy environments, but it could be a consideration in quiet settings.
- Audio Fidelity: While bone conduction technology has improved significantly, it generally doesn’t match the fidelity of high-end traditional headphones, particularly in the bass frequencies. This is due to the inherent challenges of transmitting sound through bone. The CTM ORUN1 does a great job, but the physics are different.
The Future of Bone Conduction
Bone conduction technology is constantly evolving. Researchers and engineers are working on ways to:
- Improve Sound Quality: New transducer designs and materials are being developed to enhance fidelity and reduce sound leakage.
- Reduce Size and Weight: Future bone conduction headphones are likely to be even smaller and lighter.
- Integrate Additional Features: We might see bone conduction headphones with features like built-in sensors for health tracking, or even integration with augmented reality (AR) devices. Imagine receiving directions or notifications directly through bone conduction while keeping your ears open to the world!
- Expand Applications: Bone conduction technology has potential applications beyond headphones, including:
- Hearing Aids: For people with certain types of hearing loss, bone conduction can provide a more effective way to hear.
- Underwater Communication: Bone conduction works well underwater, making it a potential solution for divers and swimmers.
- Military and Law Enforcement: Bone conduction headsets can allow personnel to maintain situational awareness while receiving communications.

Conclusion: A New Way to Listen
Bone conduction technology offers a unique and valuable alternative to traditional headphones. The CTM ORUN1, with its open-ear design, comfortable fit, and robust features, is a compelling example of this technology in action. It’s not just about listening to music; it’s about staying connected to the world around you while enjoying a safe and immersive audio experience. By understanding the science behind bone conduction, we can appreciate the innovation and potential of this fascinating technology, opening our ears – and our minds – to a new way to listen. The CTM ORUN1 isn’t just selling headphones; they’re offering a different way to interact with the auditory world.



























































