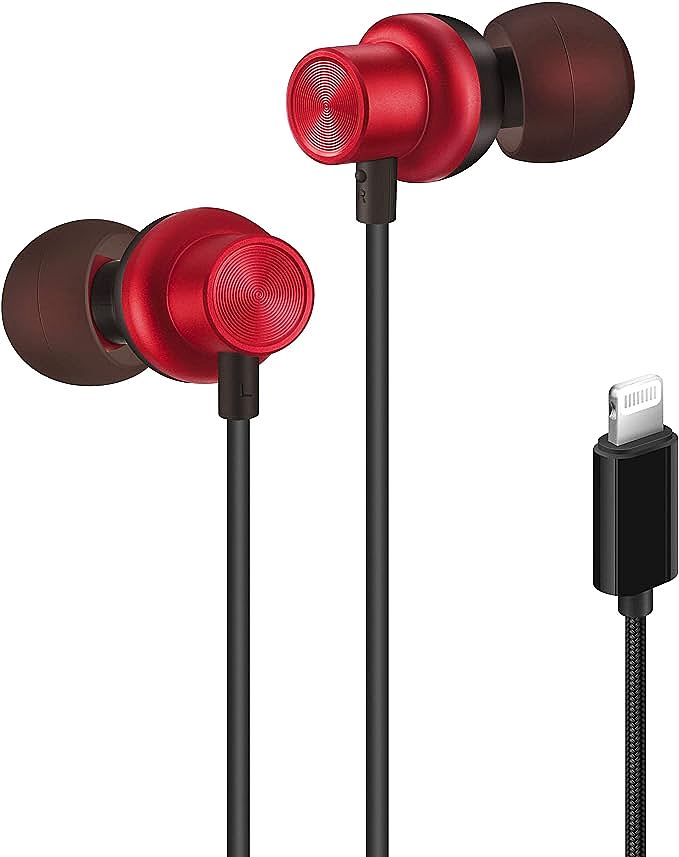
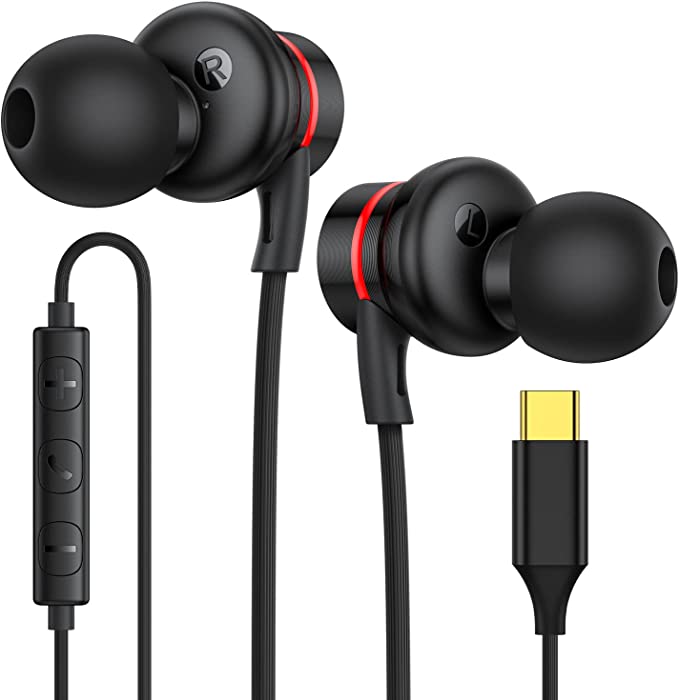
PALOVUE SweetFlow Lightning Earphones: Crisp, Clear Audio for Your iPhone
Update on Aug. 24, 2025, 5:49 p.m.
It began with a single word: “courage.” In 2016, Apple declared the venerable 3.5mm headphone jack obsolete, severing a connection that had faithfully served music lovers since the era of the Sony Walkman. In its place, we were given a tiny, infuriatingly fragile adapter—the dongle. It became a symbol of a transition that felt, to many, like a solution in search of a problem. We entered an awkward age of compromise, tethered by a weak link that seemed destined to fray, fail, or simply vanish into the ether.
Yet, quietly, amidst the rise of wireless pods and the frustration of dongle life, a different kind of solution emerged. It looks unassuming—a simple pair of wired earbuds, like the PALOVUE SweetFlow, that sells for less than a movie ticket. But to dismiss it is to miss the point entirely. This is not a relic of the past. It is a direct descendant of that “courageous” decision, and packed within its humble plastic shell is the entire story of a digital audio revolution. It is a case study in how complex science and clever engineering can solve a very human problem, affordably. To understand this $17 device is to understand the invisible world of digital sound that now surrounds us.
The Digital Stream and the Analog Wave
Before the iPhone 7, the journey of a song to your ears was an analog one, at least in its final, crucial step. Inside your phone, a specialized chip called a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) would translate the song’s digital file—a pristine stream of ones and zeros—into a continuous electrical wave. This analog signal was a physical mimic of the sound wave itself. It then traveled out the 3.5mm jack, up your headphone cable, and into the drivers that created the sound.
The problem? An analog signal is a fragile thing. Think of it as a perfect photograph being photocopied. The first copy looks great. But a copy of that copy? It’s a little fuzzier. And a copy of that copy? Degraded, noisy, and losing detail. Every inch of an unshielded cable, every low-quality connector, every nearby source of electromagnetic interference—from a power line to your Wi-Fi router—could smudge that signal, adding a fine layer of static or hiss. It was, by its very nature, a vulnerable journey.
The Lightning connector changed the entire landscape. When you plug in a Lightning earphone, the device doesn’t send out an analog sound wave. It sends out the original, perfect digital blueprint—the raw stream of ones and zeros. The sound is no longer being translated inside the phone. The data travels, pure and uncorrupted, down the cable. This is a fundamental shift. The signal that reaches the earphones is identical to the one stored in the phone’s memory. The photocopy machine has been thrown out.

The Translator’s New Home
If the digital data travels all the way to the earphones, where does the translation to sound happen? This brings us to the ghost in the machine: a tiny, crucial DAC that no longer lives in the phone, but is now housed inside the headphone’s Lightning connector itself.
This relocation is a far bigger deal than it sounds. It means that every pair of Lightning headphones must be a self-contained audio system, complete with its own DAC and its own amplifier to power the speakers. And this is precisely where Apple’s “Made for iPhone/iPod/iPad” (MFi) certification becomes critically important.
The MFi badge isn’t a mere marketing sticker. It is a seal of approval signifying that the manufacturer has used Apple-sanctioned components and has passed a battery of rigorous tests. For audio, it means the tiny DAC and amplifier tucked inside that stainless-steel-framed connector meet Apple’s minimum standards for performance, power efficiency, and safety. It ensures this miniature audio system won’t just work, but will function harmoniously with the iPhone’s software, allowing the in-line controls—volume, play, pause, Siri—to communicate flawlessly. It’s the gatekeeper that separates a reliable piece of engineering from a cheap knock-off that could produce erratic sound or, worse, damage your device. It is the guarantee that the digital translator is speaking the language correctly.

Anatomy of a Sound-Maker
Once the pristine digital signal has been translated into a clean analog wave by the MFi-certified DAC, the final act begins. Inside each earpiece of the SweetFlow lies a 10-millimeter dynamic driver. This is the heart of the headphone, a miniature loudspeaker operating on a principle of electromagnetism you learned in high school physics. An electrical current (the audio signal) flows through a finely wound voice coil attached to a flexible diaphragm. This coil sits in a magnetic field created by a permanent magnet. As the current fluctuates, it creates a shifting magnetic field that interacts with the permanent magnet, causing the coil and the attached diaphragm to vibrate rapidly back and forth. These vibrations create pressure waves in the air—the sound that you hear.
While the 10mm size offers a physical advantage in moving enough air to create a solid bass response, the final sound is a testament to the art of tuning. Engineers carefully select the diaphragm material, magnet strength, and enclosure acoustics to shape the frequency response. This is why some headphones sound “warm” and others “bright”—it is a series of deliberate engineering choices.
The same thoughtful design applies to the components you can’t hear, but definitely use. The in-line microphone is a marvel of miniaturization known as a MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) microphone. Instead of a traditional diaphragm, it uses a microscopic, silicon-based sensor that is incredibly sensitive, power-efficient, and highly resistant to the vibrations that travel up a headphone cable—the reason your voice sounds clearer on calls. The cable itself, coated in durable TPE and woven from oxygen-free copper, is chosen to withstand thousands of twists and tugs while ensuring the signal from the DAC to the driver remains as pure as possible.

The Theater Inside Your Head
Ultimately, a headphone’s job is to create a convincing illusion for your brain. And one of the greatest enemies of this illusion is outside noise. This is where we step into the realm of psychoacoustics—the science of how we perceive sound.
Our brains are constantly performing a kind of audio triage. In a noisy environment, like a subway car or a busy street, your brain prioritizes the loudest, most persistent sounds. This is a survival mechanism called the “masking effect.” The low-frequency rumble of the train’s wheels can literally render the subtle notes of a cello or the deep resonance of a bass guitar inaudible. Your brain simply doesn’t have the bandwidth to process both, so it discards the quieter sound. The music is still there, but it’s being masked.
This is where the simple, physical design of an in-ear headphone becomes so crucial. By creating a snug seal in your ear canal with the right-sized silicone tip, you are creating a barrier. This passive noise isolation physically blocks a significant portion of that ambient noise from ever reaching your eardrum. It lowers the “noise floor,” pulling back the curtain of low-frequency rumble and allowing the masked details in your music to step forward. It isn’t fancy electronic noise cancellation, but it is highly effective acoustic physics in action, clearing the stage for the performance.
The Elegance of the Everyday
No one will argue that a $17 headphone can compete with a multi-hundred-dollar audiophile setup. That is not its purpose. Some listeners might find its sound signature a little “tinny” or sharp in the high frequencies—a common trade-off in budget driver tuning. But to judge it on those terms is to miss the beauty of its solution.
The PALOVUE SweetFlow and others like it are not just products; they are elegant answers to a specific engineering challenge of our time. They represent a masterful balance of trade-offs—cost, durability, and the undeniable sonic advantages of a direct digital audio path. They solved the dongle problem not by reinventing the wheel, but by perfecting it, using certified, reliable technology to create a product that is, for millions of people, simply better than the alternative.
The most profound technologies are not always the most expensive or complex. Sometimes, they are the ones that disappear into the fabric of our daily lives, quietly and reliably doing a difficult job. They are the ghosts in the machine, the unsung triumphs of engineering that just work.